Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Overview
In this topic, we will study nucleophilic addition reactions, reduction, oxidation, reaction due to α-hydrogen and various other named reactions in detail.
Important Questions on Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
Reduction of the carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones on treatment with hydrazine followed by heating with potassium hydroxide is known as
Reaction of cyclohexanone with dimethylamine in the presence of catalytic amount of an acid forms a compound if water during the reaction is continuously removed. The compound formed is generally known as –
A mixture of benzaldehyde and formaldehyde on heating with an aqueous solution gives.
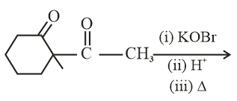
The product is
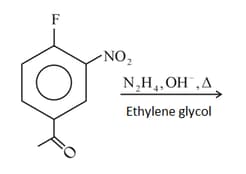
The product of the above reaction is:
Write the structure of carbonyl compound and ammonia derivative that combine to give following imine.
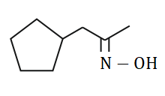
Write the structure of carbonyl compound and ammonia derivative that combine to give following imine.
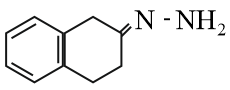
Write the structure of carbonyl compounds and ammonia derivatives that combine to give the following image.
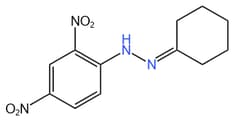
Glucose on reaction with Fehling solution gives
Which of the following reaction, will not give a yellow precipitate?
The order of susceptibility of nucleophilic attack on aldehydes follows the order
Benzaldehyde can be converted to benzyl alcohol in concentrated aqueous solution using
The alcohol that results when acetaldehyde is reacted with in the presence of dry ether and the product is hydrolysed.
Find the number of products obtained by the cross cannizzaro reaction in them.
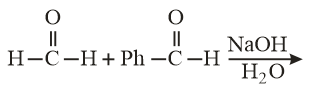
Clemmensen reduction
Which of the following properties of the carbonyl group allows aldehydes and ketones to undergo nucleophilic addition reactions?
Which of the following method is used for conversion of the ketone to hydrocarbon?
Compounds and in the following reaction are _____.
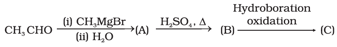
Which of the following method is used for conversion of ketone to hydrocarbon?
When ethanal is heated with Fehling's solution, then the precipitate obtained is of:
